Recommended Reading

11 Minutes
React Native Debugging: Essential Tips and Best Practices
Fix Bugs Faster! Log Collection Made Easy
Debugging React Native apps can be challenging, but using the right tools and techniques makes it manageable. Here’s what you need to know:
- Key Tools: Use React Native DevTools for component inspection and debugging, Flipper for analyzing native layers and network traffic, and Chrome DevTools for JavaScript debugging.
- Performance Fixes: Enable Hermes for faster startup and lower memory usage. Use the Performance Monitor to identify rendering bottlenecks.
- Error Management: Rely on LogBox for clear warnings, Error Boundaries to isolate issues without crashing the app and Bugfender to gather logs and exception happening in your live app.
- Network Debugging: Use Flipper’s Network Inspector to analyze API requests, monitor latency, and mock responses.
- Secure Logging: Mask sensitive data and set retention policies for logs to ensure security.
- Platform-Specific Debugging: Utilize Xcode for iOS and Android Studio for Android to address native issues.
Table of Contents
Quick Comparison
| Debugging Area | Tool/Method | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript Debugging | Chrome DevTools | Breakpoints, console access |
| Component Inspection | React Native DevTools | Inspect component tree, profile components |
| Native Debugging | Flipper, IDEs (Xcode/Android Studio) | Analyze native layers, debug platform-specific issues |
| Performance Monitoring | Performance Monitor, Hermes | Real-time metrics, optimize rendering |
| Error Tracking | LogBox, Error Boundaries and Bugfender | Clear error messages, isolate issues, gather logs and exceptions |
| Network Debugging | Flipper Network Inspector | Inspect API requests, mock responses, monitor latency |
| Secure Logging | Custom Logging Frameworks | Mask sensitive data, set retention policies |
React Native Debugging: From JS to Native

Installing Debug Tools
Set up key debugging tools to efficiently pinpoint and resolve issues in your React Native projects.
React Developer Tools Setup
To get started with React Developer Tools, follow these steps:
- Install the package:
npm install --save-dev react-devtools - Update your
package.json: Add a script to launch the DevTools.{ "scripts": { "devtools": "react-devtools" } } - Run the DevTools: Launch the tools using the following command:
npm run devtools
Once this is done, you can integrate Flipper for more advanced debugging features.
Flipper Setup Guide
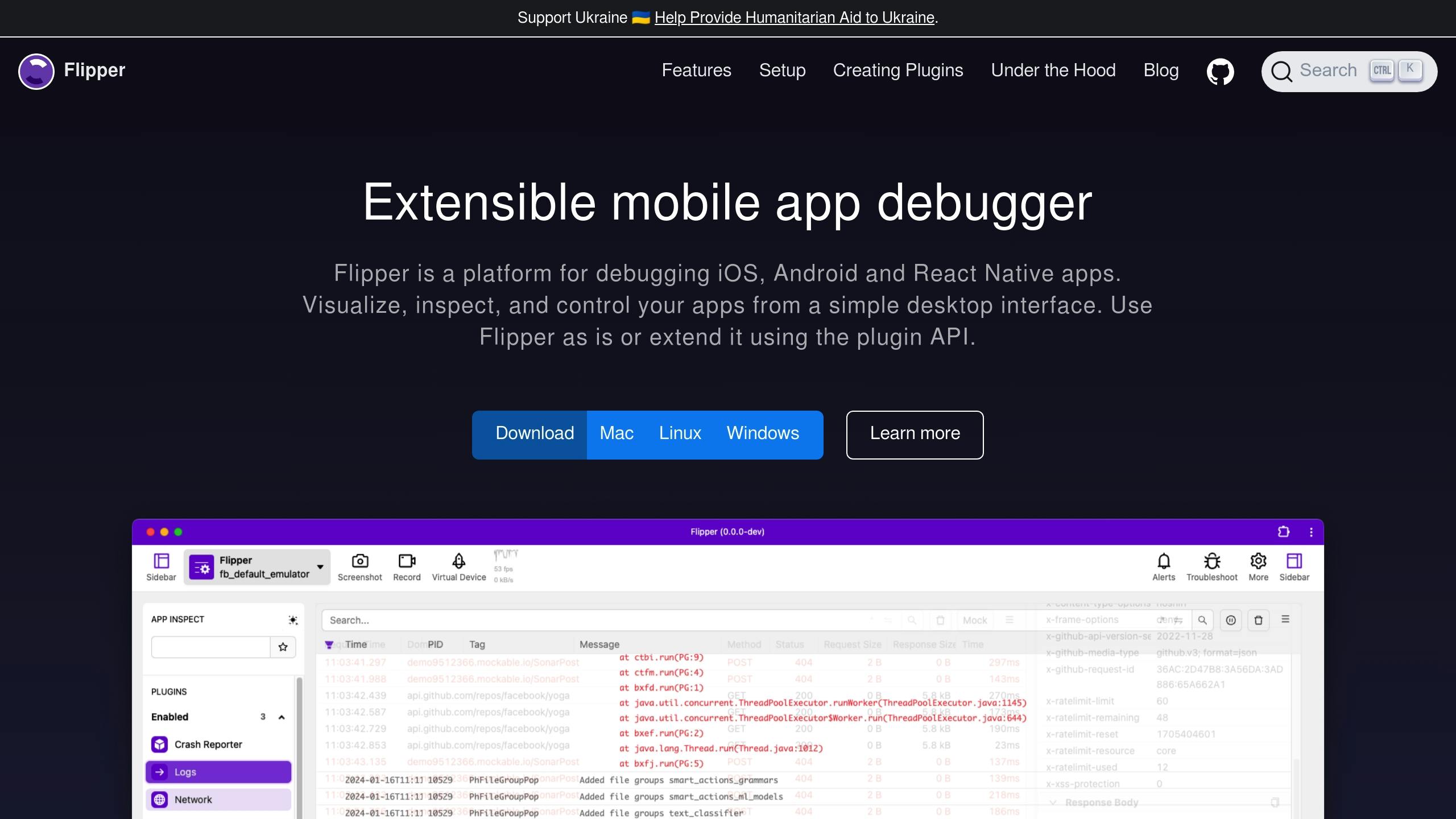
Flipper provides deeper insights into native layers of your React Native app. Here’s how to set it up:
For iOS projects: Update your ios/Podfile with the following dependencies:
pod 'Flipper', '~> 0.125.0'
pod 'Flipper-DoubleConversion'
pod 'Flipper-Folly'
pod 'Flipper-Glog'
pod 'Flipper-PeerTalk'For Android projects: Add these dependencies to your android/app/build.gradle file:
dependencies {
debugImplementation("com.facebook.flipper:flipper:${FLIPPER_VERSION}")
debugImplementation("com.facebook.flipper:flipper-network-plugin:${FLIPPER_VERSION}")
}With Flipper configured, move on to setting up the Chrome Debugger for JavaScript debugging.
Chrome Debugger Setup
To debug JavaScript in your app, follow these steps:
- Run your app: Use one of the following commands to start your app on the desired platform:
npx react-native run-ios # or npx react-native run-android - Access the developer menu:
- On an iOS simulator: Press
Cmd+D - On an Android emulator: Press
Cmd+M - On a physical device: Shake the device
- On an iOS simulator: Press
- Enable remote debugging: From the developer menu, select Debug JS Remotely. This will open Chrome DevTools for debugging.
Fixing Common React Native Issues
Speed and Performance Issues
Performance hiccups can ruin the user experience, so addressing them is a top priority. One effective way to enhance performance is by using Hermes, a JavaScript engine designed to improve startup times, reduce memory usage, and shrink app size. Additionally, the Performance Monitor in the Dev Menu offers real-time metrics for rendering performance and memory usage on both Android and iOS.
Here’s how you can monitor and improve performance:
- Enable Hermes: Activate Hermes in your project to see immediate benefits.
- Use the Performance Monitor: Turn on the overlay to track performance data as you test.
- Profile Components: Use the collected data to identify slow components and optimize them accordingly.
Once performance is optimized, it’s equally important to have strong error-handling measures in place to ensure app stability.
Error Management
React Native’s LogBox system provides a clear and effective way to manage and visualize errors. It helps identify and address critical issues before they affect the end user. Fatal errors remain visible until resolved, making debugging easier.
To manage errors effectively:
Set Up LogBox Settings
Filter out unnecessary warnings to focus on what truly matters:
LogBox.ignoreLogs(['specific warning message']); // Ignore specific warnings
LogBox.ignoreAllLogs(); // Use this only during development
Use Error Boundaries
Prevent the entire app from crashing by isolating errors in specific components:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
Bugfender.log('error', {
error: error,
info: errorInfo
});
}
// Additional component logic here
}Integrate Bugfender
Tracking errors in production is just as important as handling them during development. While LogBox and error boundaries help during development, tools like Bugfender give you much better insight into real-world issues.
Bugfender collects logs and exceptions from your users’ devices, helping you spot problems you might not see during testing. This way, you can fix bugs faster and make your app more stable for everyone.
Network and API Debug
Debugging network and API issues is a crucial step in ensuring your app runs smoothly. Tools like Flipper’s Network Inspector make it easy to analyze network traffic, helping you identify and resolve API-related problems. With Flipper, you can:
- Inspect requests and responses in detail.
- Analyze headers and payloads.
- Monitor network latency to spot slow responses.
- Mock API responses to test various scenarios.
Here’s an example of logging network requests:
fetch('<https://api.example.com/data>')
.then(response => {
console.log('Status:', response.status);
return response.json();
})
.catch(error => {
Bugfender.error('API Error:', error);
});
Using Flipper’s network plugin, you can:
- Track all inbound and outbound traffic.
- Examine headers and request bodies for troubleshooting.
- Filter requests based on type or status.
- Mock responses to simulate different API conditions during testing.
High-Level Debug Methods
Advanced debugging techniques can make tackling platform-specific issues and integrating with CI/CD pipelines much more efficient.
Platform-Specific Code Debug
When debugging platform-specific code, it’s essential to utilize both native debugging tools and JavaScript debuggers. A practical approach is to use Platform.select() with conditional breakpoints to pinpoint issues effectively.
For example, here’s how you might handle iOS-specific debugging:
if (Platform.OS === 'ios') {
Bugfender.log('debug', {
deviceInfo: Platform.constants,
buildVersion: Platform.Version
});
}
For native modules, tools like Xcode and Flipper are invaluable for inspection tasks. These tools help diagnose problems in areas such as:
- Communication across the JavaScript bridge
- Native module implementations
- Data type mismatches
- Serialization issues
On Android, Android Studio’s native tools paired with React Native’s JavaScript debugger can provide deep insights. Additionally, integrating Radon IDE with VSCode can speed up the debugging process.
After isolating platform-specific problems, these debugging practices should be incorporated into your CI/CD pipeline to ensure ongoing quality checks.
CI/CD Debug Integration
Incorporating debugging into your CI/CD pipeline requires balancing detailed error tracking with maintaining performance.
Here’s how environment-specific logging might look:
// Configure environment-specific logging
const debugConfig = {
development: {
logLevel: 'verbose',
asyncLogging: false
},
staging: {
logLevel: 'warning',
asyncLogging: true
},
production: {
logLevel: 'error',
asyncLogging: true
}
};
By tailoring logging levels – verbose for development, warnings for staging, and errors for production – you can automate CI/CD responses based on severity:
| Severity Level | Use Case | CI/CD Action |
|---|---|---|
| Debug | Development insights | Log only |
| Info | Status updates | Log and notify |
| Warning | Potential issues | Flag build |
| Error | Critical problems | Fail build |
To avoid slowing down the main thread, logging tasks should run asynchronously during tests.
Additionally, setting up error boundaries in your React components allows for capturing detailed stack traces and device information. Here’s an example:
class CIErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
Bugfender.error('CI Error', {
error: error,
info: errorInfo,
platform: Platform.OS,
buildNumber: process.env.BUILD_NUMBER
});
}
// Additional boundary logic
}
This approach ensures that errors are thoroughly tracked without compromising build performance. It helps teams detect and resolve issues early, reducing the likelihood of problems making it into production.
Debug Guidelines
Ensuring a smooth debugging process is key to maintaining reliable React Native applications. Below, we break down some essential practices to streamline your debugging workflow.
Secure Log Management
When it comes to logging, security should always be a priority. Here’s an example of a secure logging configuration:
const logConfig = {
debug: {
mask: ['password', 'token'],
retention: '24h',
async: true
},
production: {
mask: ['*'],
retention: '7d',
async: true
}
};
// Example of secure logging implementation
const secureLog = (level, message, data) => {
const maskedData = maskSensitiveData(data, logConfig[level].mask);
Bugfender.log(level, {
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
message,
context: maskedData
});
};
To maintain secure logging practices, keep these points in mind:
- Encrypt data: Ensure logs are encrypted both when stored and during transmission.
- Mask sensitive data: Use masking to protect details like passwords, tokens, or other private information.
- Set retention periods: Define how long logs are stored based on your environment (e.g., shorter durations for development and longer for production).
- Control access: Use role-based access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view or manage logs.
By securing your logs, you create a foundation for proactive error detection and resolution.
Live Error Monitoring
“Effective logging doesn’t just make debugging faster; it pinpoints the root causes of problems, saving you countless hours” [1].
Take your error monitoring to the next level by enhancing your error boundary setup. Real-time notifications based on error severity can make a huge difference. For instance:
- Critical errors: Trigger immediate alerts to the development team.
- Non-critical issues: Log these for later review, allowing you to prioritize fixes effectively.
This approach ensures urgent problems are addressed quickly while still keeping track of less pressing issues.
Code Testing and Speed Checks
Regular performance testing is essential to catch bottlenecks early. Automated testing routines can help you measure performance metrics during a component’s lifecycle.
Focus on establishing performance benchmarks for key operations, such as:
- Component render times
- Network request durations
- Memory usage
Conclusion
Main Points
Debugging in React Native has become more efficient with the introduction of modern tools. Starting with React Native DevTools (v0.76+), developers can now access features like integrated component inspection, performance profiling, and JavaScript debugging.
Here are the key components of an effective debugging workflow:
- Development Environment: Use VSCode with React Native Tools and ESLint for a smoother coding experience.
- Performance Monitoring: Keep an eye on real-time performance metrics.
- Error Management: Rely on LogBox for clear error visualization and resolution.
These elements form the foundation of a robust debugging strategy. The next step? Put these tools into practice.
Getting Started
Here’s a quick reference to essential debugging areas and their tools:
| Debug Area | Primary Tool | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | React Native DevTools | Breakpoint debugging and console access |
| Components | React Developer Tools | Inspect and analyze the component tree |
| Performance | Performance Monitor | Real-time performance metrics overlay |
| Error Tracking | LogBox | Displays warnings directly in the app |
To improve your debugging process, focus on these actions:
- Development Setup: Install React Native v0.76+ to access the latest debugging features.
- Logging Strategy: Use structured logging with severity levels and data masking to make logs more actionable.
- Performance Tracking: Enable real-time performance monitoring to identify bottlenecks early.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using Hermes in React Native, and how do you enable it?
Hermes brings a host of performance perks to React Native apps, such as reduced memory usage, smaller download sizes, and quicker startup times. These improvements directly impact the time to interactive (TTI), making apps feel more responsive and delivering a smoother experience – especially for those with more intricate features.
Here’s the best part: Hermes is enabled by default in React Native. If you’re working with the latest version, your app is already tapping into Hermes’ performance enhancements. For older projects, it’s easy to turn it on – just tweak your app’s build settings to include Hermes.
How can I use Flipper for network debugging in my React Native app?
Flipper’s Network plugin is a handy tool for keeping an eye on and troubleshooting network activity in your React Native app. It allows you to see all outgoing network requests, along with their responses, headers, and body content. You can even dig into gzipped responses and sort traffic by domain, HTTP method, or status code.
This tool simplifies spotting problems like failed requests, incorrect payloads, or unexpected response data, making it faster to fix network-related bugs in your app.
How can I securely handle logging in React Native projects, especially when dealing with sensitive data?
When working on React Native projects, safeguarding sensitive data during logging is essential. Start by making it a priority to never log sensitive details such as user credentials, personal information, or payment data unless absolutely necessary. In cases where logging can’t be avoided, make sure to mask or redact sensitive information – for instance, showing only the last four digits of a credit card number instead of the full number.
Another effective approach is using hashing techniques to log a non-reversible version of sensitive data rather than the raw data itself. This way, even if someone gains access to the logs, they won’t be able to retrieve the original information. To further protect your users and their data, always adhere to encryption best practices and ensure compliance with relevant data protection laws. These steps not only strengthen security but also help maintain user confidence in your application.
Expect The Unexpected!
Debug Faster With Bugfender


